What is Huffman coding?
Huffman coding is a compression algorithm that assigns shorter binary codes to more frequent characters in an input string, optimizing data size.
Huffman decoding is to recover the original text from the binary code generated from the huffman coding process.
Using the Huffman algorithm, we compress the input string by encoding it with the generated codes, and later decompress the binary code to recover the original string.
How Can I Build a Huffman Tree and Use It for Encoding and Decoding?
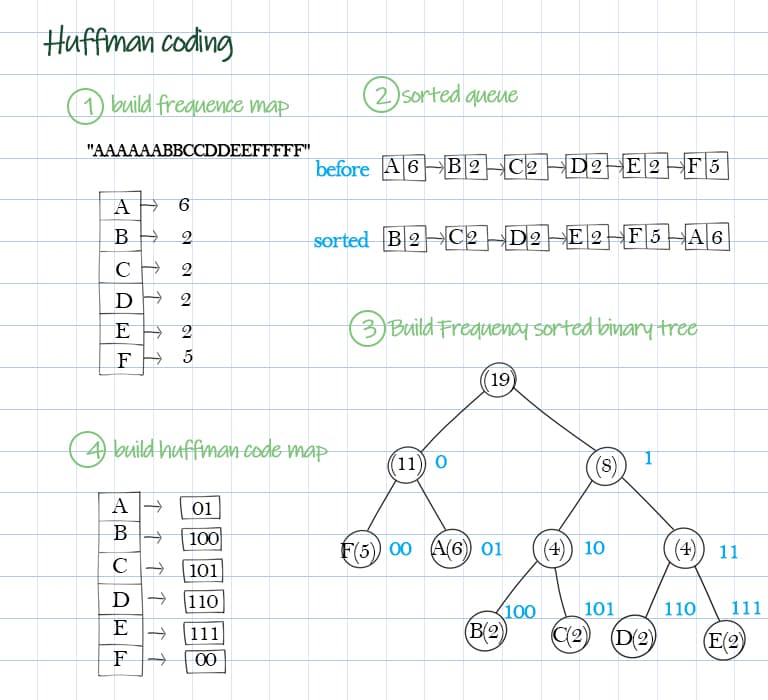
- Build a frequency map from the input string for each character.
First we construct a frequency map from the input string. Then create a queue of nodes, which contains the char and its frequency. Sort this queue by their frequency. We can see this queue as priority queue. The node with lowest frequency has highest priority.
- Build a queue of characters sorted by their frequency showing in the string.
Next is to construct the binary tree from the sorted queue. Starting from the low frequency characters, take two characters as leaves and form a subtree. Build tree from the bottom up, until all characters have been included as leaves. A finished tree has n nodes, n=2*m-1.
- Build frequency-sorted binary tree based on the sequence of elements in the queue.
After the tree is built, now traverse the tree to generate a dictionary which maps the char to binary code. The path from the root to that character (leaf) is the binary code for that character, such as A(01), B(100). Bit ‘0’ means going to the left child, bit ‘1’ means going to the right child. This is the preorder of the tree. Please note the huffman code in not necessary unique.
- create Huffman code map from the tree.
Once the frequency-sorted binary tree and the Huffman code map is generated, we can encode the input string to binary code (compressed) by using the huffman code map. We can decode the binary code to the original string (uncompressed) by using the binary tree.

- encode the input string to binary code (compressed) by using the huffman code map.
Use a for loop to go through each character in the string, use it as key to get the code from the map, concatenate them as output binary string.
- Decode the binary code to the original string (uncompressed) by using the binary tree.
This is the opposite of the last step. It is to convert back to the original string by using the same huffman code in step 4.
Amazon Interview Question
Implement the Huffman compression algorithm as shown in the example below:
1) Given a string AAAAAABBCCDDEEFFFFF, group them according to the number of occurrences: A => 6, B => 2, C => 2, D => 2, E => 2, F => 5
2) Put the string in a tree-like structure:
3. Output the Huffman code.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 | import java.util.*; class HuffmanNode { char ch; int frequency; HuffmanNode left; HuffmanNode right; //constructor, Time O(1) Space O(1) HuffmanNode(char ch, int frequency, HuffmanNode left, HuffmanNode right) { this.ch = ch; this.frequency = frequency; this.left = left; this.right = right; } // Time O(1) Space O(1) @Override public String toString() { return "(" + ch + ", " + frequency + ")"; } } public class HuffmanCoding { HuffmanNode root; //All steps to create huffman code public Map<Character, String> getCode(String input) { Map<Character, Integer> freqMap = buildFrequencyMap(input); LinkedList<HuffmanNode> queue = sortByFrequency(freqMap); root = buildTree(queue); Map<Character, String> codeMap = createHuffmanCode(root); return codeMap; } //Step 1: Create char frequency map from input string, Time O(s) Space O(m), //s is number of chars in input string, m is number of unique chars private Map<Character, Integer> buildFrequencyMap(String input) { Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) { char ch = input.charAt(i); map.put(ch, map.getOrDefault(ch, 0)+1); } return map; } //Step 2: Create queue of nodes from map and sort by frequency, Time O(mlogm) Space O(m) private LinkedList<HuffmanNode> sortByFrequency(Map<Character, Integer> map) { LinkedList<HuffmanNode> pq = new LinkedList<HuffmanNode>( ); for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { pq.add(new HuffmanNode(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue(), null, null)); } pq.sort((a,b) -> a.frequency - b.frequency); return pq; } //Step 3. Build frequency-sorted binary tree from sorted queue, return root //Time O(m) Space O(n), m is unique chars in string, n is nodes in tree n=2m-1 private HuffmanNode buildTree(Queue<HuffmanNode> nodeQueue) { while (nodeQueue.size() > 1) { HuffmanNode node1 = nodeQueue.remove(); HuffmanNode node2 = nodeQueue.remove(); HuffmanNode node = new HuffmanNode(' ', node1.frequency + node2.frequency, node1, node2); nodeQueue.add(node); } return nodeQueue.remove(); } //Step 4. Create Huffman code map by preorder of the tree, Time O(n) Space O(m+n) private Map<Character, String> createHuffmanCode(HuffmanNode node) { Map<Character, String> map = new HashMap<Character, String>(); createCodeRec(node, map, ""); return map; } //Preorder of the tree using recursion, Time O(n) Space O(n), n is number of nodes in the tree private void createCodeRec(HuffmanNode node, Map<Character, String> map, String s) { if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { map.put(node.ch, s); return; } createCodeRec(node.left, map, s + '0'); createCodeRec(node.right, map, s + '1' ); } //Step 5. Use huffman code to encode the input string, Time O(s) Space O(o), //s is input string length, o is output string length public String encode(Map<Character, String> codeMap, String input) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) { sb.append(codeMap.get(input.charAt(i))); } return sb.toString(); } //Step 6. decode. Time O(o), Space O(s), o is coded message length, s is original message input public String decode(String coded) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); HuffmanNode curr = root; for (int i = 0; i < coded.length(); i++) { curr = coded.charAt(i) == '1' ? curr.right : curr.left; if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null) { sb.append(curr.ch); curr = root; } } return sb.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) { String input="AAAAAABBCCDDEEFFFFF"; HuffmanCoding huffman = new HuffmanCoding(); Map<Character, String> codeMap = huffman.getCode(input); System.out.println("code: " + codeMap); String encoded = huffman.encode(codeMap, input); System.out.println("encoding string: " + encoded); String decode = huffman.decode(encoded); System.out.println("decoding string: " + decode); } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 | class HuffmanNode { //constructor, Time O(1) Space O(1) constructor(ch, frequency, left, right) { this.ch = ch; this.frequency = frequency; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } class HuffmanCoding { //All steps to create huffman code getCode(input) { var freqMap = this.buildFrequencyMap(input); var nodeQueue = this.sortByFrequence(freqMap); this.root = this.buildTree(nodeQueue); var codeMap = this.createHuffmanCode(this.root); return codeMap; } //Step 1: Create char frequency map from input string, Time O(s) Space O(m), //s is number of chars in input string, m is number of unique chars buildFrequencyMap(input) { var map = new Map(); for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) { let ch = input.charAt(i); if (!map.has(ch)) { map.set(ch, 1); } else { let val = map.get(ch); map.set(ch, ++val); } } return map; } //Step 2: Create queue of nodes from map and sort by frequency, Time O(mlogm) Space O(m) sortByFrequence(map) { var queue = []; for (let entry of map.entries()) queue.push(new HuffmanNode(entry[0], entry[1], null, null)); queue.sort((a,b) => a.frequency - b.frequency ) return queue; } //Step 3: Build frequency-sorted binary tree from sorted list, return root //Time O(m) Space O(n), m is unique chars in string, n is nodes in tree n=2m-1 buildTree(nodeQueue) { while (nodeQueue.length > 1) { //build tree from ground up starting from low frequency let node1 = nodeQueue.shift(); let node2 = nodeQueue.shift(); let node = new HuffmanNode('', node1.frequency + node2.frequency, node1, node2); nodeQueue.push(node); } return nodeQueue.shift(); } //Step 4: Create Huffman code map by preorder of the tree, Time O(n) Space O(m+n) createHuffmanCode(node) { var map = new Map(); this.createCodeRec(node, map, ""); return map; } //Preorder of the tree using recursion, Time O(n) Space O(n), n is number of nodes in the tree createCodeRec(node, map, s) { if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { map.set(node.ch, s); return; } this.createCodeRec(node.left, map, s + '0'); this.createCodeRec(node.right, map, s + '1' ); } //Step 5. Use huffman code to encode the input string, Time O(s) Space O(o) //s is input string length, o is output string length encode(codeMap, input) { var s = "" for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) { s += codeMap.get(input.charAt(i)); } return s; } //Step 6: decode //Time O(o), Space O(s), o is coded message length, s is original message input decode(coded) { var s = "" var curr = this.root; for (let i = 0; i < coded.length; i++) { curr = coded.charAt(i) == '1' ? curr.right : curr.left; if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null) { s += curr.ch; curr = this.root; } } return s; } } var input = "AAAAAABBCCDDEEFFFFF" var huffman = new HuffmanCoding(); var codeMap = huffman.getCode(input); console.log(codeMap); var encoded = huffman.encode(codeMap, input); console.log("encoding string: " + encoded); var decode = huffman.decode(encoded); console.log("decoding string: " + decode); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 | class HuffmanNode : #constructor, Time O(1) Space O(1) def __init__(self, ch, frequency, left, right) : self.ch = ch self.frequency = frequency self.left = left self.right = right # Time O(1) Space O(1) def __str__(self): return "(" + str(self.ch) + ", " + str(self.frequency) + ")" class HuffmanCoding : # All steps to create huffman code def getCode(self, input) : freqMap = self.buildFrequencyMap(input) nodeQueue = self.sortByFrequence(freqMap) self.root = self.buildTree(nodeQueue) codeMap = self.createHuffmanCode(self.root) return codeMap #Step 1: Create char frequency map from input string, Time O(s) Space O(m), #s is number of chars in input string, m is number of unique chars def buildFrequencyMap(self, input) : map = {} for c in input: map[c] = map.get(c,0) + 1 return map #Step 2: Create queue of nodes from map and sort by frequency, Time O(mlogm) Space O(m) def sortByFrequence(self, map) : queue = [] for k, v in map.items(): queue.append(HuffmanNode(k, v, None, None)) queue.sort(key = lambda x: x.frequency) return queue #Step 3: Build frequency-sorted binary tree from sorted queue, return root #Time O(m) Space O(n), m is unique chars in string, n is nodes in tree n=2m-1 def buildTree(self, nodeQueue) : while len(nodeQueue) > 1: node1 = nodeQueue.pop(0) node2 = nodeQueue.pop(0) node = HuffmanNode('', node1.frequency + node2.frequency, node1, node2) nodeQueue.append(node) return nodeQueue.pop(0) #Step 4: Create Huffman code map by preorder of the tree, Time O(n) Space O(m+n) def createHuffmanCode(self, node) : map = {} self.createCodeRec(node, map, "") return map #Preorder of the tree using recursion, Time O(n) Space O(n) def createCodeRec(self, node, map, s) : if node.left == None and node.right == None : map[node.ch] = s return self.createCodeRec(node.left, map, s + '0') self.createCodeRec(node.right, map, s + '1') # Step 5. Use huffman code to encode the input string, Time O(s) Space O(o), # s is input string length, o is output string length def encode(self, codeMap, input) : s = "" for i in range(0, len(input)): s += codeMap.get(input[i]) return s #Step 6. decode. Time O(o), Space O(s), o is coded message length, s is original message input def decode(self, coded) : s = "" curr = self.root for i in range (0, len(coded)) : curr = curr.right if coded[i] == '1' else curr.left if curr.left == None and curr.right == None: s += curr.ch curr = self.root return s input="AAAAAABBCCDDEEFFFFF" huffman = HuffmanCoding() codeMap = huffman.getCode(input) print("code: " + str(codeMap)) encoded = huffman.encode(codeMap, input) print("encode message: " + encoded) decode = huffman.decode(encoded) print("decoding string: " + decode) |
Output:
code: {‘F’: ’00’, ‘A’: ’01’, ‘B’: ‘100’, ‘C’: ‘101’, ‘D’: ‘110’, ‘E’: ‘111’}
encode message: 0101010101011001001011011101101111110000000000
decoding string: AAAAAABBCCDDEEFFFFF
O Notation:
Time complexity: O(nlogn + m + s)
Space complexity: O(n+m+o)
s is input string length; n is number of unique chars in input; m is number of nodes in tree, m = 2n-1;
o is encoded string length.
Download HuffmanCoding.java
Download HuffmanCoding.js
Download HuffmanCoding.py