An adjacency matrix is a 2d array representing a graph. The nodes are the headings for the rows and columns. The element in the cell indicates whether an edge is present between two nodes. Depth first search (DFS) is an algorithm used to traverse or search in a graph. The algorithm goes as far away from the starting point as possible. It returns only when it finishes the job or reaches a dead end. DFS can be implemented using stack or recursion. This post gives solution of depth first search in matrix with recursion. There are two examples – Find path and Number of islands.
DFS can be implemented with recursion. It starts from the source cell and explores the adjacent cells in 4 directions (up, down, left, right). The adjacent cells are accessed by increasing or decreasing the indices of the row or the column by 1 at a time. If the cell’s value is pass, it continues further. If a cell’s all un-visited adjacent cells are blocked or beyond the edge, this is a dead end. Then the recursive method returns by the order of call stacks and explores other routes.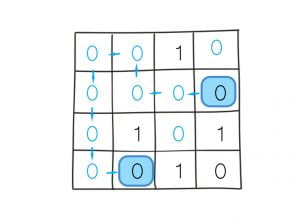
A variable visited is used to track which cell has been visited. This guarantees each cell is visited once. The time complexity down to O(m*n). m is the number of rows. n is the number of columns. This technique is called memoization.
Table of Content
1. Find whether there is path from source to destination

This example is to use DFS to find out whether there is path from the source to the destination. In the matrix, 1 represents block, 0 represents pass. The input sx and sy are the row and column of the source cell, dx and dy are the row and column of destination cell. The program returns true if there is path; returns false if not.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | public class DFSinMatrix { //Check whether there is path from src(x,y) to dest (x, y) //DFS wraper, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n) public static boolean hasPathDfs( int[][] adj, int sx, int sy, int dx, int dy) { int m = adj.length; int n = adj[0].length; boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; dfs(adj, sx,sy, visited); if(!visited[dx][dy]) { return false; } return true; } //DFS + memoization, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n) private static void dfs(int[][] adj, int i, int j, boolean[][] visited) { int m = adj.length; int n = adj[0].length; if(i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || adj[i][j] == 1 || visited[i][j]) { return; } visited[i][j] = true; dfs(adj, i-1, j, visited); // Move left dfs(adj, i+1, j, visited); // Move Right dfs(adj, i, j-1, visited); //Move top dfs(adj, i, j+1, visited); //Move bottom } public static void main(String[] args) { //2D matrix with 1's as blocked and 0's as path. int[][] matrix = {{0,0,1,0,1}, {0,0,0,0,0}, {0,1,0,1,1}, {0,0,0,0,0}}; //find path int sx = 1, sy = 3, dx = 3, dy = 1; System.out.println("Find path from (" + sx + "," + sy + ") to (" + dx + "," + dy + "): "); System.out.println("DFS: " + hasPathDfs(matrix, sx, sy, dx, dy)); } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 | class DFSinMatrix { //Check whether there is path from src(x,y) to dest (x, y) //DFS wraper, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n) hasPathDfs(adj, sx, sy, dx, dy) { var rows = adj.length; var columns = adj[0].length; var visited = []; for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { visited[i] = new Array(columns).fill(false); } this.dfs(adj, sx, sy, visited); if(!visited[dx][dy]) { return false; } return true; } //DFS + memoization, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n) dfs(adj, i, j, visited) { var rows = adj.length; var columns = adj[0].length; if (i < 0 || i >= rows || j < 0 || j >= columns || adj[i][j] == 1|| visited[i][j]) { return; } visited[i][j] = true; this.dfs(adj, i-1, j, visited); // Move left this.dfs(adj, i+1, j, visited); // Move Right this.dfs(adj, i, j-1, visited); //Move top this.dfs(adj, i, j+1, visited); //Move bottom } } var matrix = [[0,0,1,0,1], [0,0,0,0,0], [0,1,0,1,1], [0,0,0,0,0]]; var g= new DFSinMatrix(); //find path var sx = 1, sy = 3, dx = 3, dy = 1; console.log("Find path from (" + sx + "," + sy + ") to (" + dx + "," + dy + "): "); console.log("DFS: " + g.hasPathDfs(matrix, sx, sy, dx, dy)); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | class DFSinMatrix: #Check whether there is path from src(x,y) to dest (x, y) #DFS wraper, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n) def hasPathDfs(self, adj, sx, sy, dx, dy) : m = len(adj) n = len(adj[0]) visited = [[False for i in range(n)] for j in range(m)] self.dfs(adj, sx, sy, visited) if visited[dx][dy] == False: return False return True #DFS + memoization, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n) def dfs(self, adj, i, j, visited) : m = len(adj) n = len(adj[0]) if i < 0 or j < 0 or i > m-1 or j > n-1 or adj[i][j] == 1 or visited[i][j] : return visited[i][j] = True self.dfs(adj, i-1, j, visited) # Move left self.dfs(adj, i+1, j, visited) # Move Right self.dfs(adj, i, j-1, visited) # Move top self.dfs(adj, i, j+1, visited) # Move bottom matrix = [[0,0,1,0,1], [0,0,0,0,0], [0,1,0,1,1], [0,0,0,0,0]] #find path sx = 1 # source x sy = 3 # source y dx = 3 # destination x dy = 1 # destination y g = DFSinMatrix() print("Find path from (" + str(sx) + "," + str(sy) + ") to (" + str(dx) + "," + str(dy) + "): ") print("DFS: " + str(g.hasPathDfs(matrix, sx, sy, dx, dy))) |
Output:
Find path from (1,3) to (3,1):
DFS: true
O Notation:
Time complexity: O(m*n)
Space complexity: O(m*n)
m is number of rows, n is number of columns
2. Number of Islands
In a binary matrix of 0s or 1s, the island consists of 1s surrounded by 0s. Number of islands is to count the number of islands in matrix. Sometimes the question is also called “number of shape”.

Facebook Interview Question:
Given a 2d array of 0s and 1s, 0 means water, 1 means land, connected 1s form an island, count the number of islands on this map.
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}
{0, 1, 0, 0, 1}
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1}
returns 3
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | public class NumOfIslands { //DFS wrapper, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n), m is number of rows, n is number of columns public static int numOfIslands(int[][] mat) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; if (mat == null || m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; int count = 0; boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; //as memo for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (mat[i][j] == 1) { count++; dfs(mat, i, j, visited); } } } return count; } //DFS + memoization, Time O(4) ~ O(1), Space O(1), 4 directions is constant private static void dfs(int[][] mat, int i, int j, boolean[][] visited) { int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i > m-1 || j > n-1 || visited[i][j]) return; if (mat[i][j] != 1) return; mat[i][j] = 0; visited[i][j] = true; dfs(mat, i-1, j, visited); //left dfs(mat, i+1, j, visited); //right dfs(mat, i, j-1, visited); //upper dfs(mat, i, j+1, visited); //lower } public static void main(String args[]) { int[][] matrix = {{0,1,0,1,0}, {0,1,0,0,1}, {0,1,1,0,1} }; System.out.println("number of islands: " + numOfIslands(matrix)); } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | class NumOfInlands { //DFS wrapper, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n), m is number of rows, n is number of columns numOfIslands(mat) { var m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; if (mat == null || m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; var count = 0; var visited = []; //as memo for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { visited[i] = new Array(n); } for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (mat[i][j] == 1) { count++; this.dfs(mat, i, j, visited); } } } return count; } //DFS + memoization, Time O(4) ~ O(1), Space O(1), 4 directions is constant dfs(mat, i, j, visited) { var m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length; if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i > m-1 || j > n-1 || visited[i][j]) return; if (mat[i][j] != 1) return; mat[i][j] = 0; visited[i][j] = true; this.dfs(mat, i-1, j, visited); //left this.dfs(mat, i+1, j, visited); //right this.dfs(mat, i, j-1, visited); //upper this.dfs(mat, i, j+1, visited); //lower } } const matrix = [[0,1,0,1,0], [0,1,0,0,1], [0,1,1,0,1]]; var n = new NumOfInlands(); console.log("number of islands: " + n.numOfIslands(matrix)); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | class NumOfInslands: #DFS wrapper, Time O(m*n), Space O(m*n), m is number of rows, n is number of columns def numOfIslands(self, mat) : m = len(mat) n = len(mat[0]) if mat == None or m == 0 or n == 0: return 0 count = 0; visited = [[False for i in range(n)] for j in range(m)] for i in range(0, m): for j in range (0, n): if mat[i][j] == 1: count+=1 self.dfs(mat, i, j, visited) return count #DFS + memoization, Time O(4) ~ O(1), Space O(1), 4 directions is constant def dfs(self, mat, i, j, visited) : m = len(mat) n = len(mat[0]) if i < 0 or j < 0 or i > m-1 or j > n-1 or visited[i][j]: return if mat[i][j] != 1: return mat[i][j] = 0 visited[i][j] = True self.dfs(mat, i-1, j, visited); #left self.dfs(mat, i+1, j, visited); #right self.dfs(mat, i, j-1, visited); #upper self.dfs(mat, i, j+1, visited); #lower matrix = [[0,1,0,1,0], [0,1,0,0,1], [0,1,1,0,1]] n = NumOfInslands() print("number of islands: " + str(n.numOfIslands(matrix))) |
Output:
number of islands: 3
O Notation:
Time complexity: O(m*n)
Space complexity: O(m*n)
m is number of rows, n is number of columns
Download
Download DFSinMatrix.java
Download DFSinMatrix.js
Download DFSinMatrix.py
Download NumOfIslands.java
Download NumOfIslands.js
Download NumOfIslands.py
More Data Structures and Algorithms